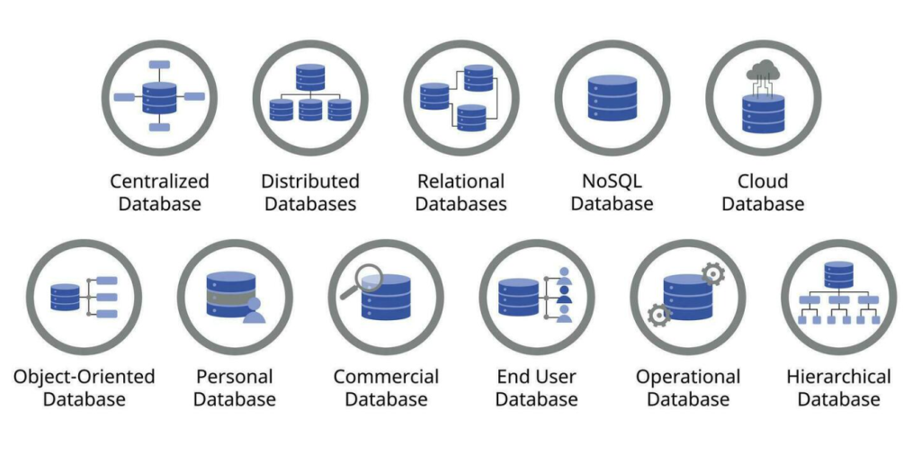
There are several classifications of databases; a database is an organized assembly of data that allows for straightforward and effective storage, retrieval, and alteration of information.
In today’s technology environment, numerous types of databases are employed, such as:
Every type of database possesses distinct strengths and weaknesses, and selecting
the appropriate type for a specific use case necessitates through evaluation of the data being stored and its intended usage.
1) Centralized database:
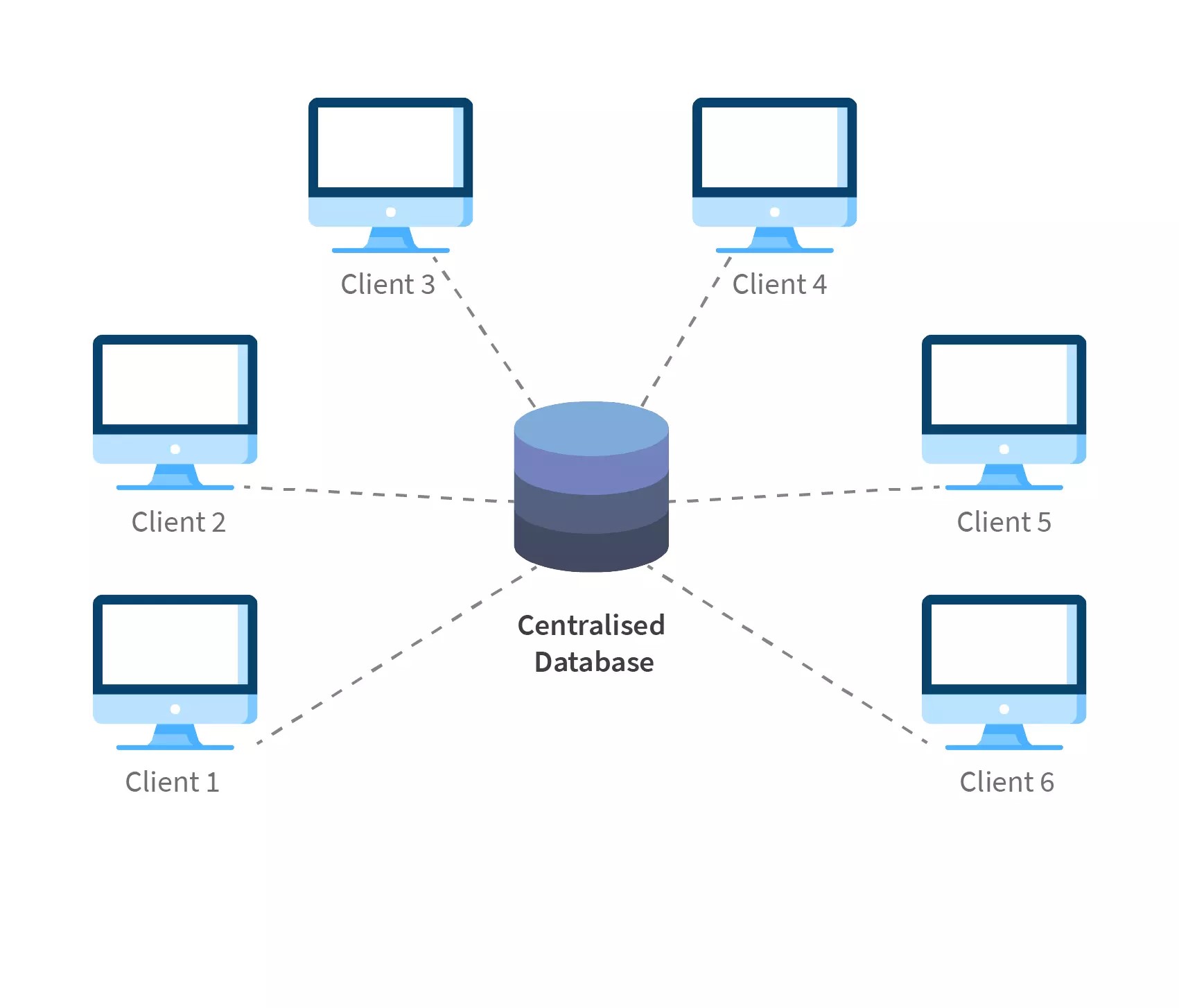
A centralized database is a repository of information located in a single place,
accessible from multiple points. The primary function of a centralized database management system is to provide facilities and access to all connected computers,
meeting the requirements requested by any individual node.
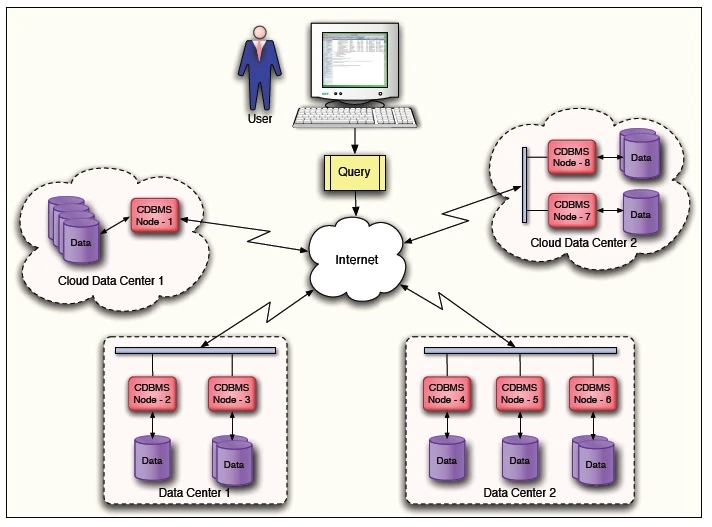
 2) Cloud database:
2) Cloud database:
A cloud database is designed to operate within a public or hybrid cloud environment,
facilitating the organization, storage, and management of data for an organization. These databases may be provided as a managed database-as-a-service (DBaaS) or installed on a cloud-based virtual machine (VM) and managed internally by the organization’s IT team.
A commercial database is developed and maintained by a commercial entity, typically made available to customers and potential clients.
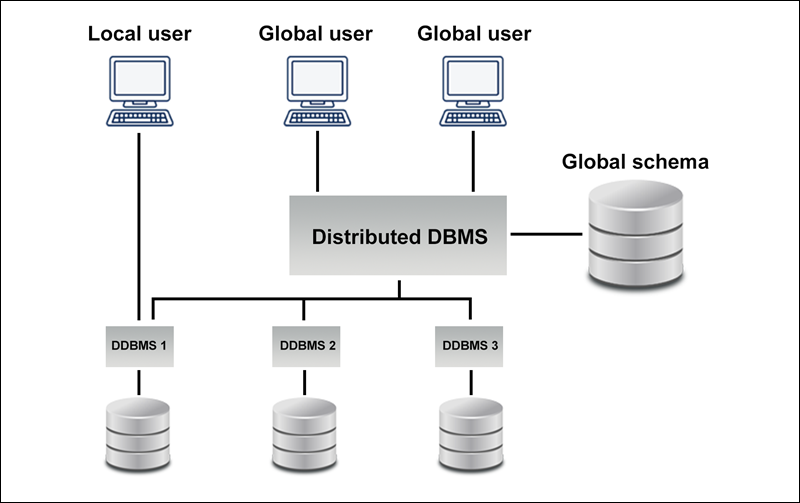
A distributed database is characterized by data being stored across various physical locations, which may include multiple computers within the same physical site or spread across a network of interconnected computers.
5) End-User database:
An end-user database allows for the storage of data generated by an end user, enabling them
to create and manage data directly, thus allowing for direct interaction with the database.
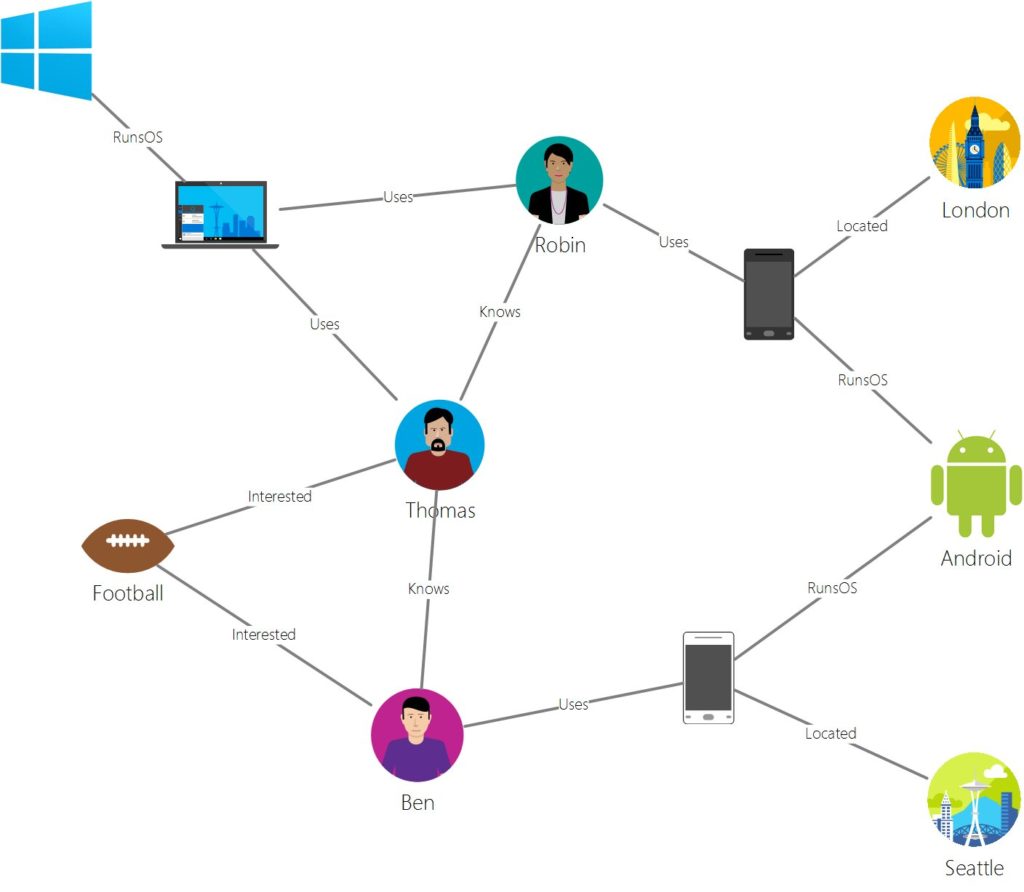
 6) Graph database:
6) Graph database:
Graph databases are purpose-built to store and navigate relationships among objects. Relationships are first-class citizens in the graph database, and most of the value of graph databases is derived from these relationships.
A graph database uses nodes to store the data entities and edges to store relationships between entities.
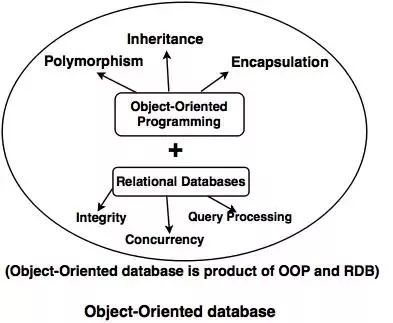
7) Object-oriented database:
The database combines object-oriented programming concepts with relational database
principles. Think of a class as a model, and objects as various constructs/instances of it. These instances share the properties they derive from the class.
Databases play a crucial role in organizing, accessing, and managing information across various systems today. Each type—whether relational, NoSQL, or in-memory—offers distinct advantages based on the specific requirements of a project. A thorough understanding of these options enables developers and businesses to make informed decisions and design solutions that are scalable, efficient, and prepared for the future. As the significance of data continues to grow, selecting the right database will remain essential for building successful applications. Keep learning and stay ahead!